Lecture Details[]
Jeff Kerr; Week 5 MED1011; Anatomy
Lecture Content[]
Inner cell mass is programmed at 8 cell stage, at this stage if it divides vertically development is normal, if it divides equatorially it is abnormal. Blastocyst has ICM and trophoblast for extraembryonic tissues. Compaction of ICM occurs at polar location in blastocoel. The blastocyst escapes from the ZP and implants into nucleus. ICM then forms two layers- ectoderm and endoderm, forming the bilaminar embryonic disc.
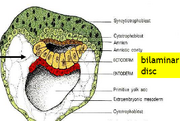
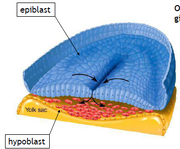
Blastocyst implants in uterus 6 days after ovulation, syncytiotrophoblast burrows into uterine wall, secretes hCG and becomes chorion. Endometrium encloses embryo. 2 weeks post conception there is an embryonic disc, amnion, ectoderm and endoderm. Embryonic disc has outer epiblast and inner hypoblast, is known as primitive endoderm and forms an extra embryonic membrane. Only the epiblast gives rise to the fetus. Epiblast cells invaginate through the primitive streak and form 3rd embryonic layer when they differentiate and muliply, they also displace cells of the hypoblast. Forms the mesoderm.
The primitive streak regresses, neutral crests approach each other and form neural fold and eventually the neural tube with neural crest cells either side. This forms the vertebral arch (lack thereof is spina bifida.
12-14 days after fertilisation is growing blastocyst implanted which has bilaminar disc; gastrulation at 15-16 days has the trilaminar embryonic disc. The ectoderm forms skin, glands, hair, nails, head connective tissue, nervous system. Mesoderm forms skeleton, muscles, kidneys, gonads, heart, vessels, blood and most connective tissue. Endoderm forms respiratory lining, gut, liver, pancreas, bladder, tonsils, para/thyroid and thymus.
Pluripotent cells are embryonic stem cells that form in the early embryo and give rise to all the tissues and organs of embryo/fetus. Embryonal carcinoma forms teratomas. Unipotent adult stem cells exist as germ cells. Multipotent AS cells are bone marrow cells. Bone marrow cells are from mesoderm. Allogenic transplants are from gene matched donor. Stem cells from cord blood, usually reserved for children. Autologous tranplants are from own patient, often before chemo.